Definition
The maturity stage of the product life cycle comes after growth, in the concept of the product life cycle. The concept implies that a product, like a living being, progresses through various stages of life. These stages include development, active growth, maturity, and decline. Marketers can use the concept to define the life cycle stage of their product and apply the most efficient marketing strategies for the given stage.
By the time a product has reached maturity it has established brand awareness, a chain of distributors, and stable sales. At the same time, competition will have entered the market.
The challenges of the maturity stage
Keeping sales volumes up
During the growth stage, sales increased at a constant rate. But by maturity, the market is usually saturated, and the sales stabilize or plateau. They may even start to drop off. For the company keeping sales volumes up is the primary challenge driving all marketing decisions.
Maintaining the market share
As the competition is high, it has become harder to maintain market share. Many manufacturers offer the same product, often, at lower prices. This is when price wars usually begin.
Retaining the profit
The product usually makes the most profit during the maturity stage. But it’s also the point at which the sales stop increasing. Marketing campaigns no longer result in any meaningful increase in revenue and they’re often just a waste of money.
Marketing Implications
Marketing emphasis
The main goal is to prolong the maturity stage, successfully getting ahead of the competition and generating profits.
At this stage, the manufacturer can benefit from high sales volumes and produce at lower costs due to economies of scale. During the growth stage, the business would have discovered more efficient, cost effective production methods, helping it to stay competitive and prolong the maturity stage.
Through applying the right strategies, it’s possible to retain and even increase the market share during maturity.
So which strategies are right?
Let's look at Marketing Mix strategy during maturity stage in terms of 4p’s.
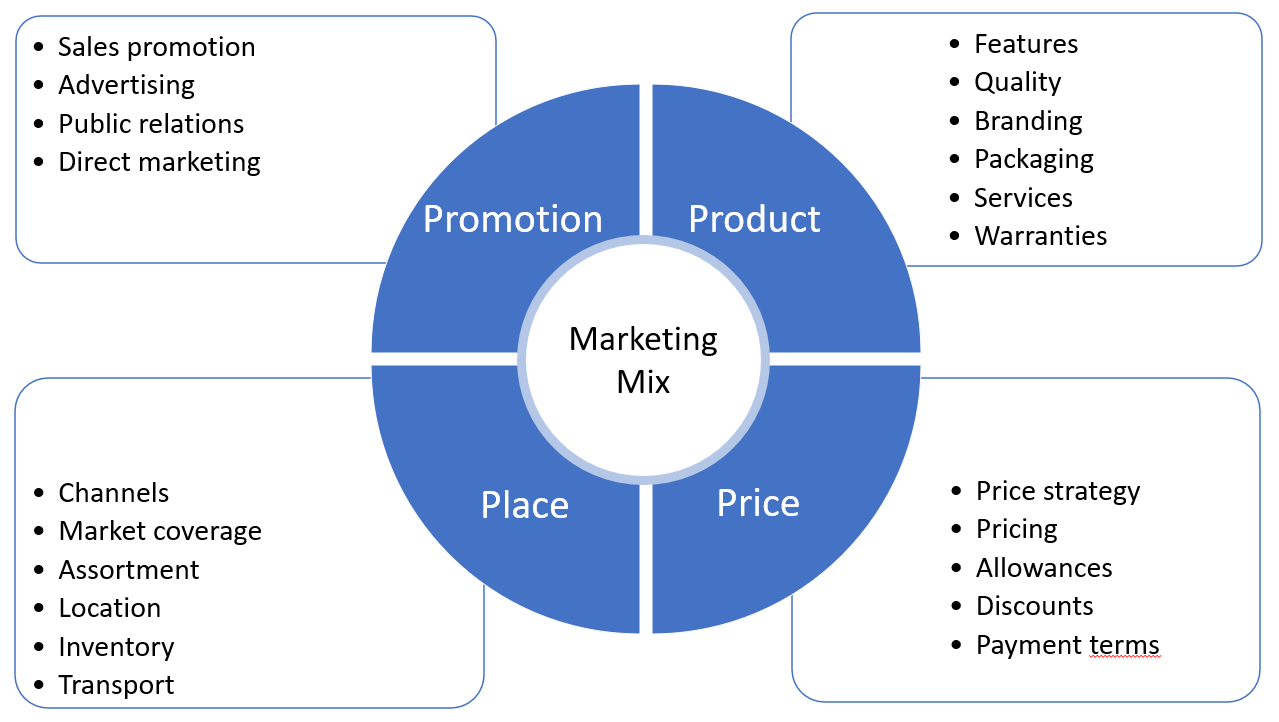
Product strategy
Most manufacturers add new features, at this stage, to diversify the product. They may make changes based on research in the existing audience or among non-users, to find out what would make the product more attractive for them. It’s still important to maintain consistent product quality and maintain the brand’s reputation.
Pricing strategy
The prices should match or beat those of the competition. Usually, at the maturity stage, the prices are lower than they were in the previous life cycle. The means of competing on price should be built into the initial pricing strategy.
Promotional strategy
Campaigns should aim at expanding the customer base. Where a company expands to other countries, they should create localized content. At this stage promotions could target new segments, for example, younger customers or new geographic regions.
Distribution strategy
The brand has to maintain distribution channels. Many companies choose to expand to new markets. They must then establish distribution channels in the new locations. While in the growth stage, the distributors would have advocated the company’s products, now they need only sell.
The maturity stage is characterized by a peak in sales and a market that is almost saturated.Marketing strategies include diversifying the product, lowering prices, and communicating to a broader audience the benefits of the given brand.



