
Table of Contents
Efficient data management is a constant pursuit for manufacturers, wholesalers, and retailers. And when it comes to achieving this efficiency, one format stands out above the rest – BMECat. Developed by the German association BME (Bundesverband Materialwirtschaft, Einkauf und Logistik e.V.) in 1999, this XML-based standard offers a powerful solution for electronic catalog data exchange.
This article will help you get a better understanding of what BMECat format is. It will provide clear examples on how it is applied in combination with various software and classification models.
What is BMECat?
It is a standardized language and structure for describing product's attributes in business-to-business (B2B) sector. By using tags, BMEcat sets up the structure for organizing data fields in electronic catalogs, guaranteeing smooth and error-free data transmission.
It relies on XML technology to facilitate the standardized exchange of multimedia catalog data and B2B product classification systems (like ETIM, ECLASS, etc.). Such file structure provides a common framework for suppliers and buyers to communicate and exchange data,streamlining the process and ensures accuracy.
How is BMECat used?
BMECat format is primarily used in commerce. The general workflow goes something like this:
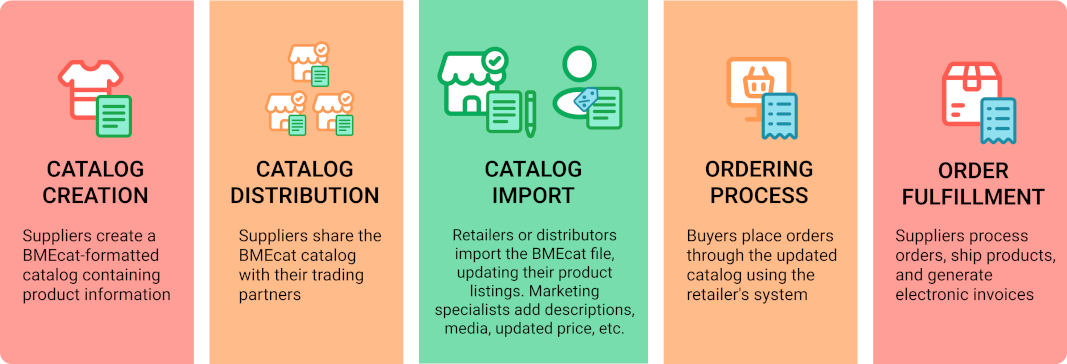
As per this example, suppliers create a detailed catalog in BMEcat format, sharing it with retailers or distributors. Partners swiftly import the data, updating their product listings. Buyers then place orders using the updated catalog, triggering order processing and fulfillment by suppliers. This cycle ensures current catalog information, streamlining B2B transactions.
BMECat is also extremely useful in sales. The format gives marketing specialists full access to the product data. Through Product Information Management (PIM) systems, they can provide media, quality descriptions and additional information not included by supplier. Such functionality helps e-shop integrate technical data, with the inherent style of the e-commerce platform.
Which software can process BMECat?
Manufacturing, tech suppliers, medical, grocery, and many other industries rely on this format. As a result, various software applications and systems have the capability to process BMEcat files. Here are a few examples:
- PIM (Product Information Management) Systems such as AtroPIM, Akeneo, Pimcore, and inRiver are commonly used to efficiently manage and exchange product information through BMEcat. You can learn more about PIM systems in our dedicated article.
- eCommerce Platforms like Adobe Commerce (Magento) and Shopware often offer extensions or modules that facilitate the import and export of BMEcat files, allowing for seamless updates to product catalogs.
- ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) Systems – SAP and Microsoft Dynamics, among other ERP systems, may integrate BMEcat support to streamline catalog management and order processing.
- EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) Systems – TrueCommerce and other EDI systems may provide support for BMEcat, enabling businesses to electronically exchange standardized catalog data.
- XML Processing Tools like Oxygen XML Editor or XMLSpy, which are designed for generic XML processing, can be utilized to view, validate, and edit BMEcat files.
- Open-Source Tools like BMEcatLib offer libraries and utilities that assist in working with BMEcat files, allowing developers to seamlessly integrate BMEcat support into their applications.
- Custom Software Solutions – Many companies develop custom software solutions tailored to their specific requirements, incorporating BMEcat processing capabilities for catalog synchronization and data exchange.
- Industry-Specific Solutions – Certain industries, such as automotive or electronics, often have specialized software solutions that support BMEcat for catalog and product data exchange.
Benefits of BMECat
BMEcat offers several benefits for businesses involved in catalog management and e-procurement.
Efficient Catalog Management
BMEcat optimizes the creation and updates of catalogs, ensuring that product information is well-organized and easily maintained. This efficiency leads to time savings for businesses, allowing them to prioritize their core operations instead of getting caught up in the complexities of catalog management.
Interoperability Across Systems
BMEcat's standardized format promotes seamless interoperability between various business systems. This means that companies can effortlessly exchange catalog data with different partners, reducing the complexities of integration and enhancing collaboration within the supply chain.
Enhanced Accuracy and Consistency
By utilizing a structured format, BMEcat minimizes errors in product information. It maintains consistency across catalogs, reducing the risk of discrepancies between suppliers and buyers. This accuracy fosters trust among trading partners and improves the overall reliability of product data.
Facilitates Electronic Data Exchange
BMEcat facilitates the electronic exchange of data between businesses, encouraging a shift from manual to automated processes. This not only speeds up order processing but also reduces the likelihood of errors associated with manual data entry, enhancing the overall efficiency of B2B transactions.
Adaptability to Diverse Industries
BMEcat's versatility allows it to be applied across various industries, ranging from manufacturing to healthcare and beyond. Its adaptability makes it a robust solution for companies with diverse product offerings, providing a standardized framework for catalog exchange regardless of the sector.
Cost-Effective Integration
The standardized nature of BMEcat simplifies integration efforts, resulting in lower costs associated with connecting different systems. This cost-effectiveness is particularly advantageous for businesses seeking to optimize their operations without making substantial investments in complex integration solutions.
Which data is transferred with BMECat?
Basic file structure consists of two main elements – Header and Transaction. Header contains the general information about the product type, suppliers, and buyers. Meanwhile, the transaction section provides specifics on various directories, including:
- Product names, descriptions, and identifiers;
- Unit prices, discounts, and currency information;
- Stock levels, lead times, and availability status;
- Dimensions, weight, and other technical attributes.
- URLs or references to images and multimedia files
- Product categories, classifications, and hierarchies
- Shipping information, packaging details, and handling instructions
- Company names, contact information, and identifiers.
- Promotional text, marketing messages, and campaign details.
- Additional, industry-specific data elements
- Product classification according to ECLASS, ETIM, proficl@ss, UNSPSC, etc.
Which BMECat versions are available?
Currently there are four versions of the format:
Version 1.0 – the first version of the BMECat. Released in 1999, quickly spread in in German-speaking countries, being the most powerful than other common formats of software manufacturers, like B. CIF 3.0 or eCX 2.0.
Version 1.2 – modified and released in 2001. The modification allowed the possibility of transferring product classification systems and was the most widespread version in mid-2005.
Version 2005 – was released in November 2005 and supposed to be a "final draft version". The main improvements include support for external catalogues, configurable products, dynamic price components and more.
Version 2005.2 – is a second revision of the format, and currently the latest one. The focus was on improved support for classification systems.
BMECat and Classification models
The BMEcat format does not imply its own classification but is oriented towards reflecting product data in accordance with as many existing models as possible. These models provide a set of specific configurable attributes, that can be reused on various products.
When BMEcat is combined with one of them, it allows for a more detailed and standardized representation. The integration of such models enhances precision and specificity of product information, making it easier for trading partners to understand and use the data consistently.
Popular classification standards such as ECLASS, proficl@ss, UNSPSC and ETIM are all supported by BMEcat. By adopting a compatible classification system, companies can ensure efficient and uniform communication within the format.
ETIM, for example, defines a set of classes and properties specific to electronic goods, while BMEcat can incorporate this classification into its structure. Even though BMEcat can be used on its own to exchange general item data, the integration with classification systems like ETIM provides additional benefits.
Conclusion
In conclusion, as manufacturers, wholesalers, and retailers seek ever greater efficiency in data management, BMECat emerges as a pivotal solution for catalog data exchange. The utility of the format extends prominently to e-procurement, e-catalog, and e-commerce platforms, facilitating streamlined B2B transactions.
The format's application in shopping, particularly in catalog creation, distribution, and import, exemplifies its impact on enhancing the efficiency of the entire supply chain. Furthermore, BMECat's versatility is evident in its usage across diverse industries.


